Demystifying AI Models: The Brains Behind Artificial Intelligence

In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force with the potential to reshape industries and human experiences. At the heart of this AI revolution lies the concept of AI models, the digital brains that power intelligent machines and applications. In this article, we’ll explore what AI models are, how they work, and their diverse applications across different domains.
Understanding AI Models
An AI model is a computational framework or algorithm designed to mimic human intelligence. These models are trained to perform specific tasks or make predictions by processing and analyzing data. The key to their effectiveness lies in their ability to identify patterns, relationships, and features in data, much like the human brain.
Types of AI Models
AI models come in various flavors, each tailored to a specific set of tasks or applications. Here are some common types:
1. Natural Language Processing (NLP) Models
NLP models, such as the Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPT), have gained significant attention. They excel in understanding and generating human language. For instance, GPT-3 can answer questions, write essays, and perform language-related tasks with remarkable fluency.
2. Computer Vision Models
Computer vision models, including convolutional neural networks (CNNs), are designed to analyze visual data like images and videos. They’re used in applications like image classification, object detection, and facial recognition.
3. Reinforcement Learning Models
Reinforcement learning models learn by interacting with an environment. They’re utilized in robotics and gaming, where they make decisions to maximize rewards over time. An example is AlphaGo, which became a Go champion through extensive reinforcement learning.
4. Recommendation Models
Recommendation models leverage user preferences and historical data to provide personalized suggestions. Whether it’s suggesting products to buy, movies to watch, or music to listen to, these models enhance user experiences.
5. Predictive Models
Predictive models make forecasts based on historical data. They’re used in fields like finance, healthcare, and meteorology to predict stock prices, disease outbreaks, and weather conditions, respectively.
How AI Models Work
The magic of AI models lies in their training process. To create a functional model, developers feed it vast amounts of relevant data. During training, the model learns to recognize and extract meaningful patterns and relationships from this data. This process involves adjusting numerous internal parameters, often represented as weights in a neural network.
Once trained, the model can make predictions or perform tasks based on new, unseen data. For instance, an image recognition model trained on thousands of cat and dog images can identify cats and dogs in new images.
Applications Across Industries
AI models have permeated various industries, offering solutions to complex problems and enhancing productivity. Here are some notable examples:
1. Healthcare
In healthcare, AI models assist in diagnosing diseases, analyzing medical images, and even predicting patient outcomes. They enable faster and more accurate diagnoses, improving patient care.
2. Finance
The financial sector uses AI models for fraud detection, algorithmic trading, and risk assessment. These models help institutions make data-driven decisions and manage financial risks.
3. Entertainment
Streaming platforms like Netflix and Spotify rely on recommendation models to suggest content to users. These models personalize user experiences by offering tailored content recommendations.
4. Transportation
Self-driving cars use computer vision and reinforcement learning models to navigate roads and make real-time driving decisions. These models enhance safety and efficiency in transportation.
The Ongoing Evolution of AI Models
AI models are continuously evolving. Researchers and developers work tirelessly to improve their performance, expand their capabilities, and make them more accessible. OpenAI’s GPT-3, which gained fame for its language prowess, has already been succeeded by GPT-4, showcasing the rapid pace of advancement in AI technology.
Conclusion
AI models are the digital brains powering the AI revolution. They enable machines and applications to understand language, interpret images, make decisions, and provide valuable insights across various domains. As AI continues to advance, we can expect AI models to play an increasingly integral role in shaping the future of technology and society, unlocking new possibilities and transforming the way we live and work.
Business Listings Related to the Article: Demystifying AI Models: The Brains Behind Artificial Intelligence
Vision India Services
Vision India Services Pvt Ltd remains a forefront trailblazer in furnishing staffing and Human Resources Management solutions that aptly address the ever-shifting and distinct requisites of businesses spanning the globe.
- Category
- Business Services
MyClassboard
MyClassboard is an advanced school ERP software, meticulously crafted to streamline and optimize the entire school management process. At its core, this innovative solution comprises a comprehensive collection of modules, thoughtfully engineered to seamlessly automate various administrative tasks.
- Category
- Education & Training
More Articles Like: Demystifying AI Models: The Brains Behind Artificial Intelligence
AI and Quantum Computing: A Powerful Combination
In recent years, both Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Quantum Computing have emerged as groundbreaking technologies with the potential to revolutionize various industries. While AI has already made significant advancements in areas such as machine learning and data analysis, Quantum Computing is still in its early stages of development. However, when these two technologies converge, the possibilities become truly extraordinary. […]
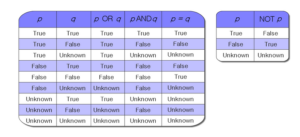
Exploring Three-Valued Logic Models: Beyond True and False
In the realm of logic and computer science, binary logic is the foundation upon which most systems are built. It operates on the basic principle of truth and falsehood, where statements are either true (1) or false (0). However, there are scenarios where a more nuanced approach is required to represent uncertainty or incomplete information. […]
Understanding Network Slicing in 5G: Unleashing the Power of Customization
The advent of 5G technology has brought with it a promise of revolutionary changes in the way we connect, communicate, and experience the digital world. Among the groundbreaking features that 5G introduces, network slicing stands out as a concept that has the potential to reshape the telecommunications landscape. In this article, we’ll delve into what […]